
Rigenerazione urbana e processi partecipativi
An interview (in Italian) to our senior researcher Lorenzo Tripodi made by the social innovation program CheFare

An interview (in Italian) to our senior researcher Lorenzo Tripodi made by the social innovation program CheFare
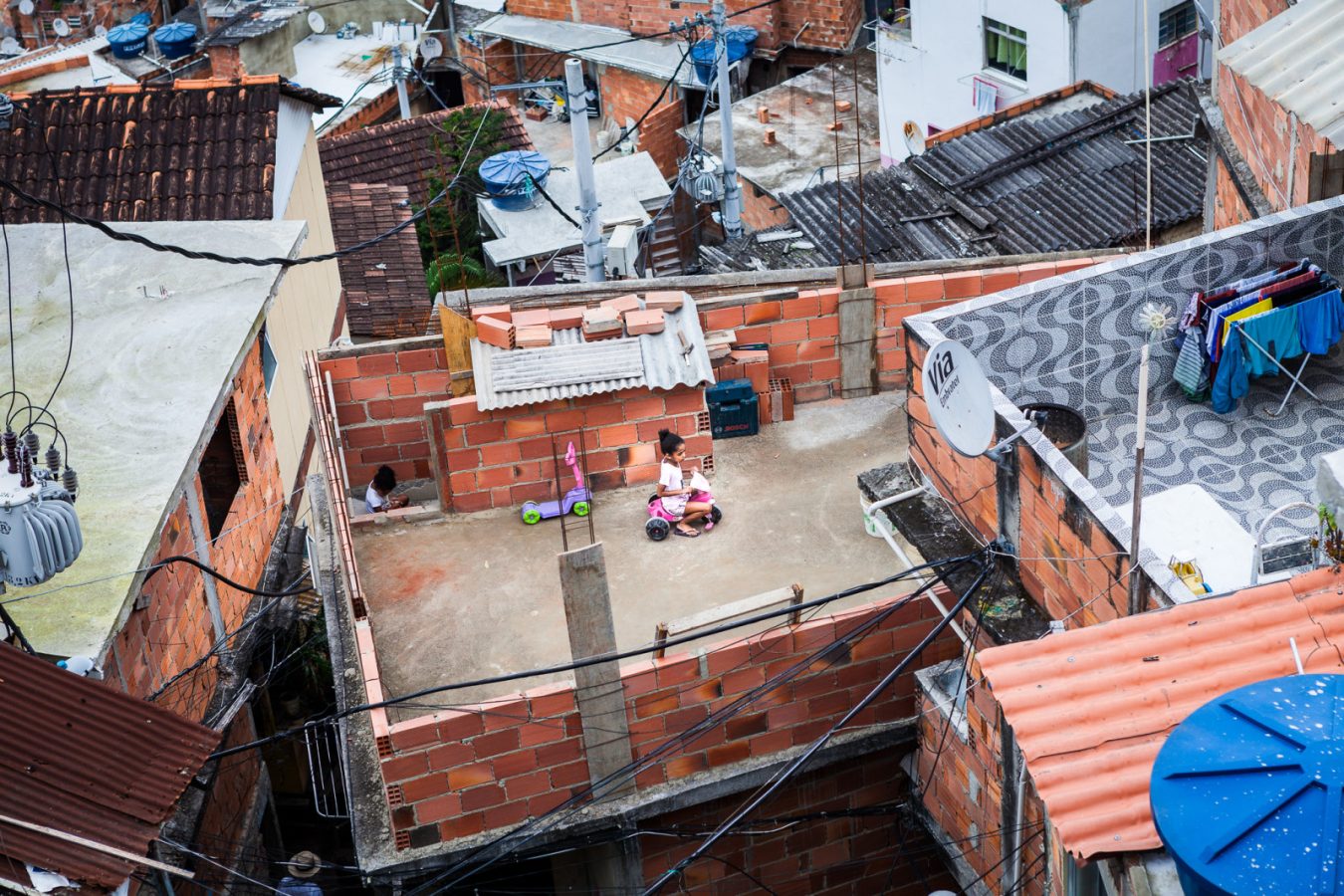

From July 30 to August 5 the “Santa Marta Sem Fronteiras” cocreation workshop took place in Rio de Janeiro. Five days of activities and site visits in the Santa Marta favela involved more than 20 researchers from the partners organisations. Manuela Conti and Sergio Segoloni took part as representatives of Tesserae. The program coordinated by local community organisers and the […]

Interdisciplinary Conference 14-15 September 2017 University of Bath Faculty of Humanities and Social Sciences Creative projects shape cities. They have the power to challenge negative connotations attached to disadvantaged neighbourhoods, transform the cityscape and residents’ lives for the better, and create opportunities for dialogue between various urban actors including artists, residents and decision makers. Artist-led […]
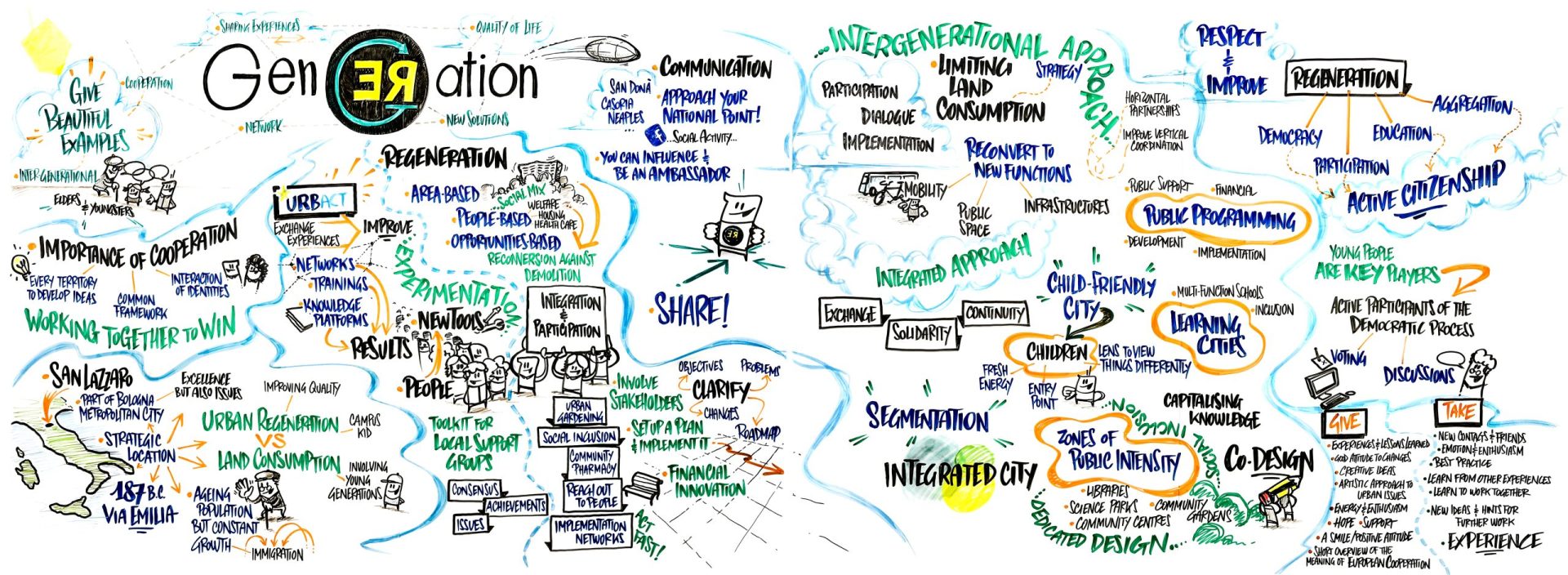
On February 27/28 the Kick Off meeting of the ReGeneration URBACT III Implementation Network has taken place in San Lazzaro di Savena. The lead partner city has presented the project to regenerate a central area of the city into a multifunctional open campus comprising schools, sport facilities heater and public space. The stakeholders involved in […]
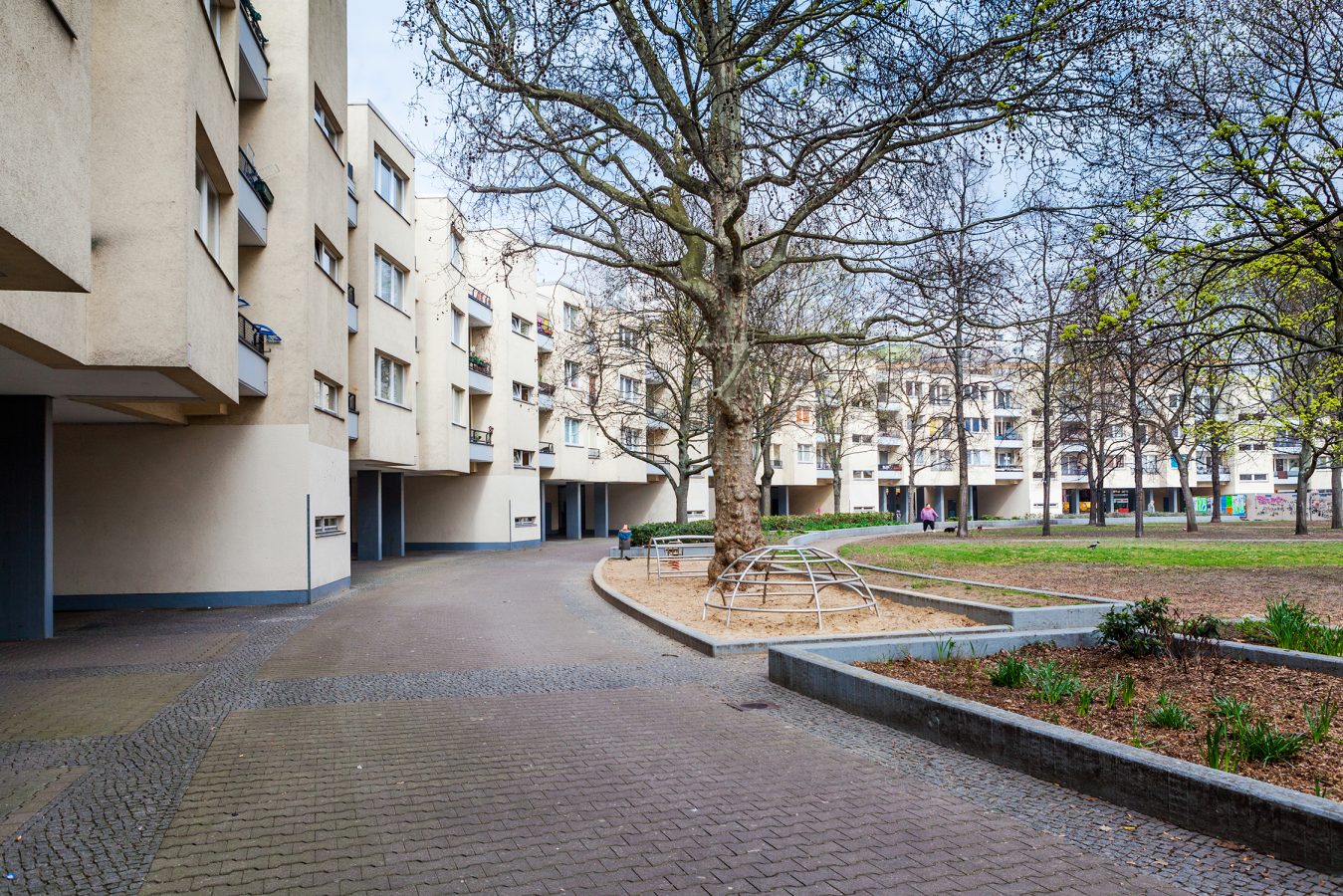

Suffering from its marginalized position during the years of the German division, the neighborhood was recognized and labelled as a deprived area in 2005 due to its low standards of economic development, its poor social integration and quality of life. These characteristics made the territory of Südliche Friedrichstadt a periphery in the centre of Berlin, as the area is located in the proximity of some of the city’s main attractive spots, such as the lively Mitte and the creative Friedrichschain-Kreutzberg. In a twenty-year time-span, a set of policies of local urban renewal has been gradually implemented to re-centralize the neighborhood, starting from the very re-centralization of the role of its residents in directly participating in small decision-making processes. This served to acknowledge, create and institutionalize their identity as a geo-social collectivity. Commercial, leasure and creative initiatives have begun to flourish in the area, projecting it as an emblem of juxtapositions and contradictory tendencies characterizing modern urban contexts, whereby transitions to new lifestyles are mediated by old identites and latent risks of gentrification, displacement and social conflicts.
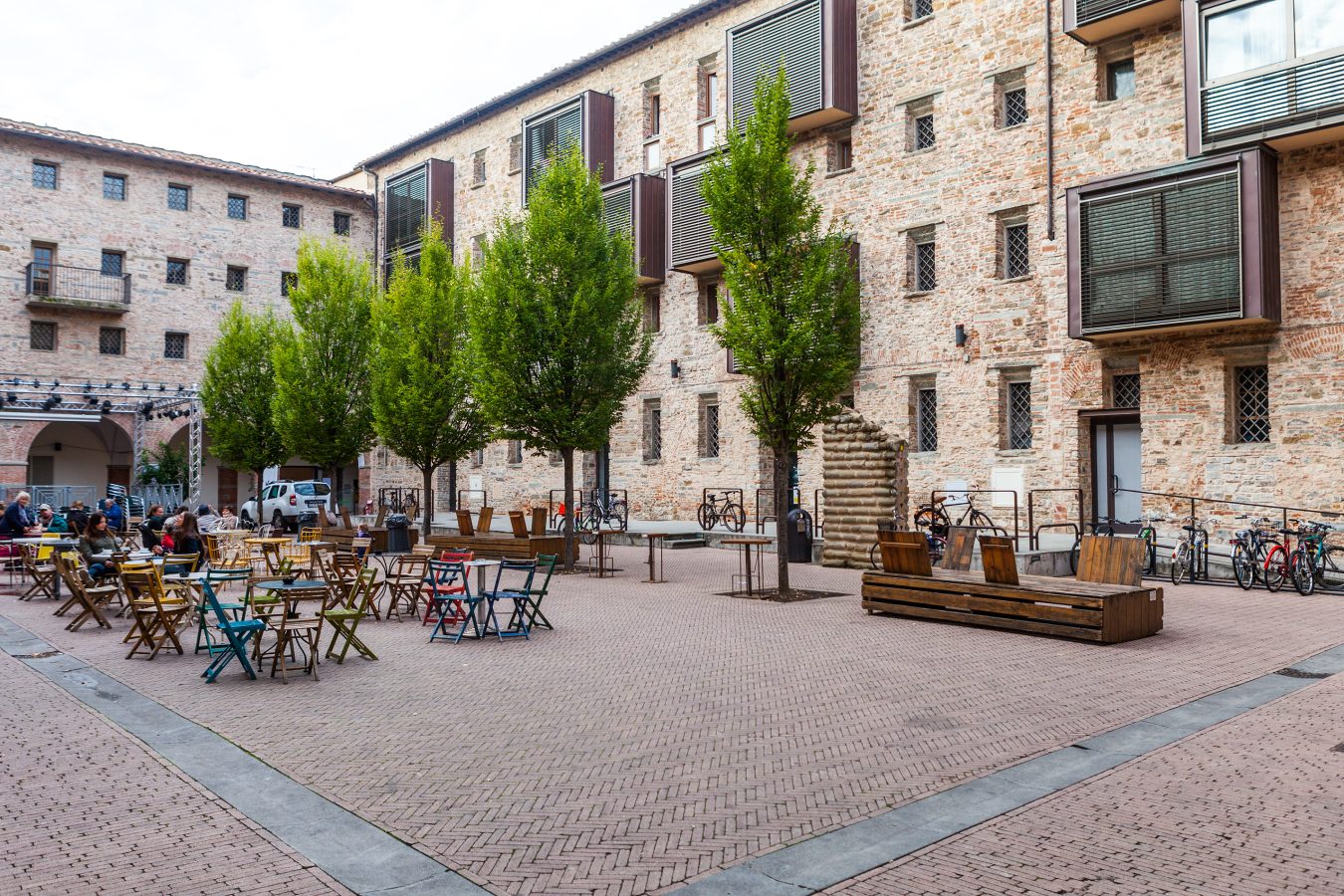

The regeneration of the ancient prison complex of Le Murate in the historical centre of Florence is a successful experience of integrated planning, which has restored an area that has historically been cut off from the urban and social fabric of the Santa Croce neighbourhood.
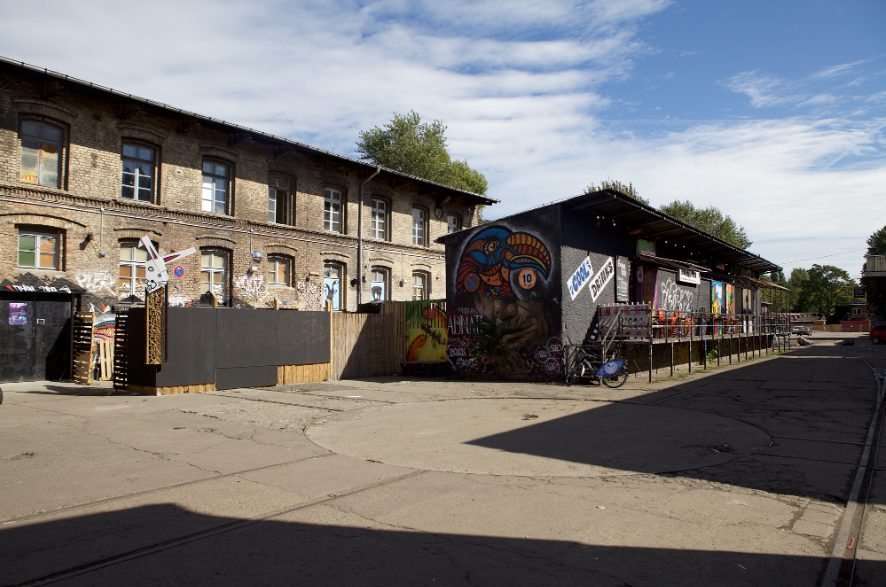

A Prussian railway workshop, a Cold War industrial wasteland, a contemporary socio-cultural center in the heart of Berlin Friedrichshain. The area is emblematic of collective and informal processes of creative transfomation reinventing Berlin’s urban landscape. The R.A.W. in Berlin-Friedrichshain was originally serving as a railway workshop in the XIX century. After being damaged during World War II and undergoing various transformations, it became a neglected wasteland in post-unification Berlin. In 1999, the RAW-Tempel association repurposed the site for artistic and cultural activities, aiming to create a vibrant hub for creativity and community engagement. In 2015, the Kurth Group acquired ownership of R.A.W. and recognized its potential for investment and urban development. Unlike other financial actors, the new owner aimed to respect the site’s identity and socio-cultural programs, giving long-term residents more control over their pre-existing properties. Establishing a participatory approach to urban planning, new plans for the R.A.W. Tower, a 100-meter-tall building, was set to be constructed starting in 2024. The project is intended to blend with older activities, integrating new offices, green areas, markets, and other services, with the R.A.W.’s role as a cultural institution. However, concerns about power dynamics and possible future compromises between top and bottom interests revolving around the R.A.W. might still challenge the current collaborations between the community and external investors.