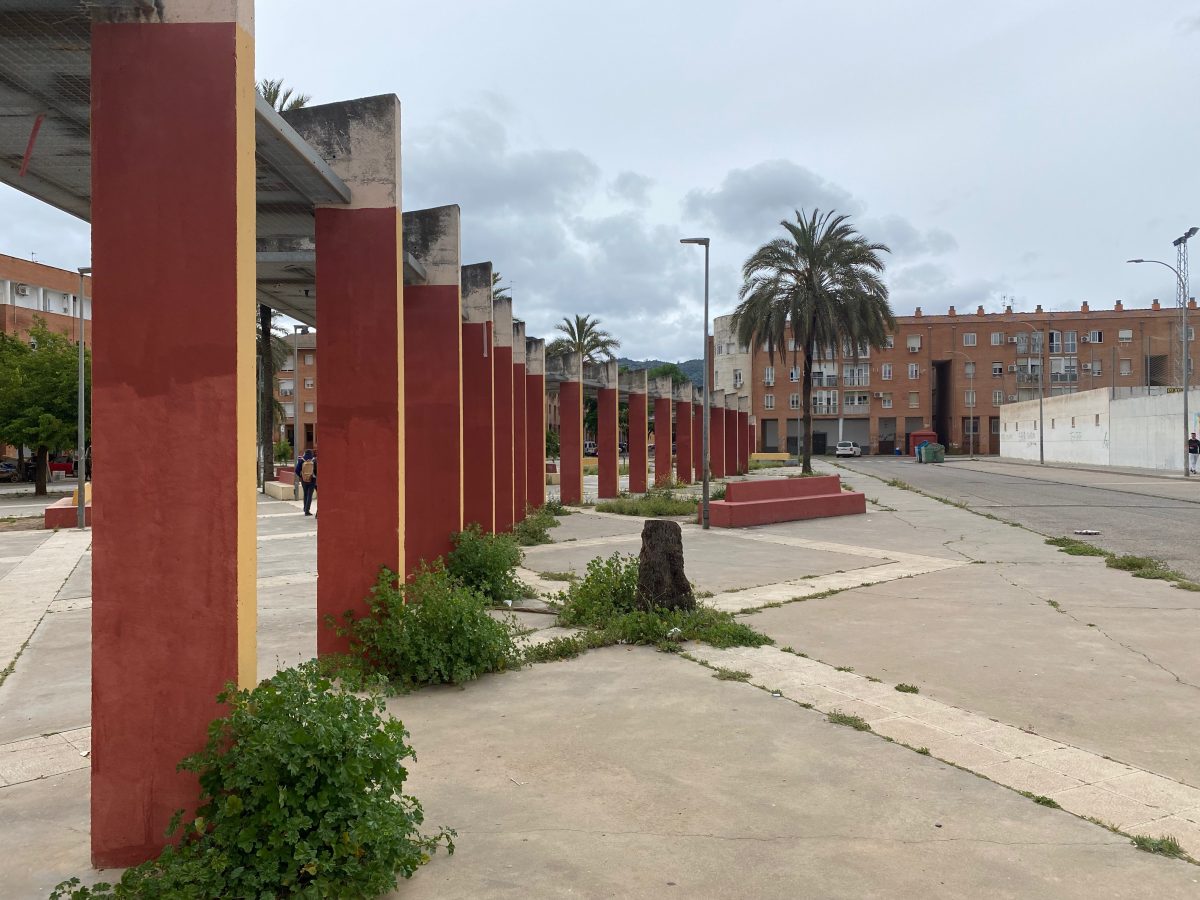
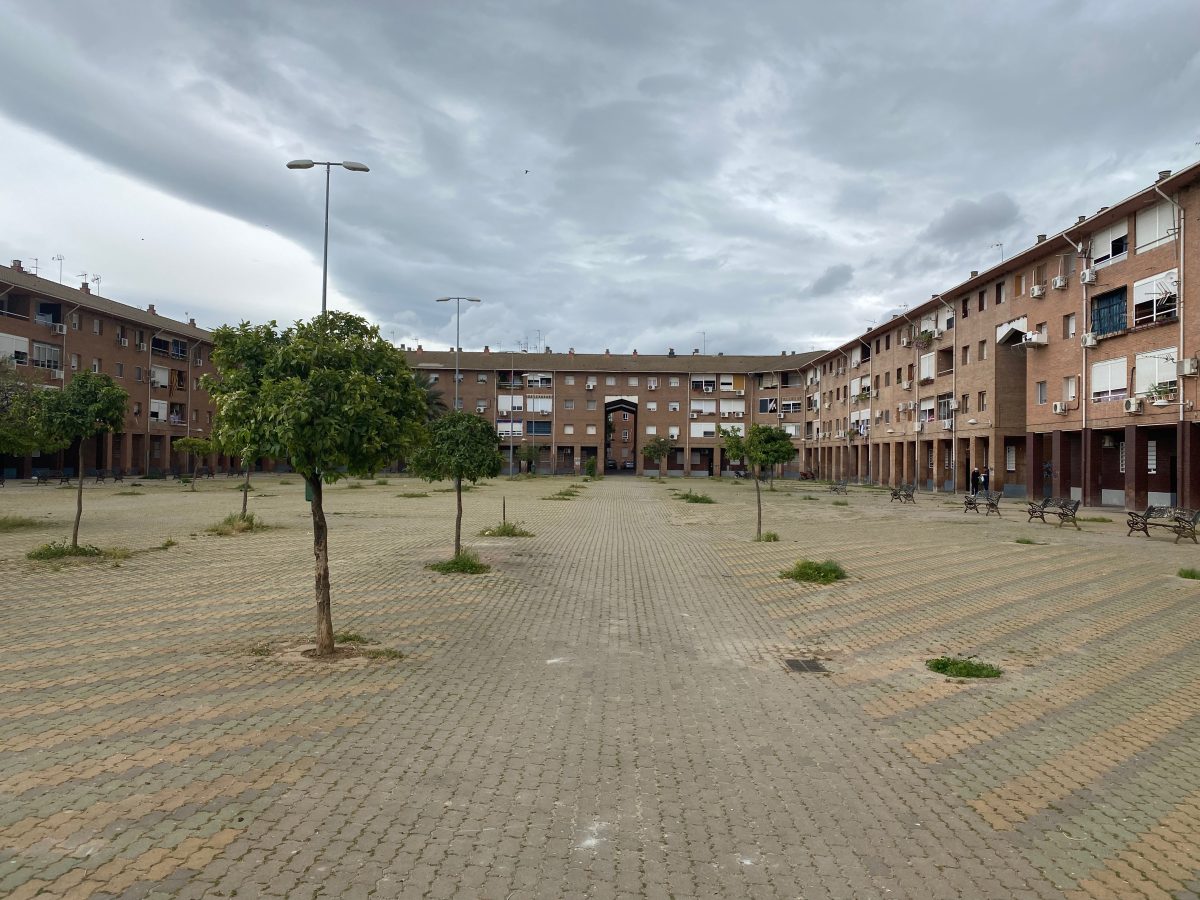
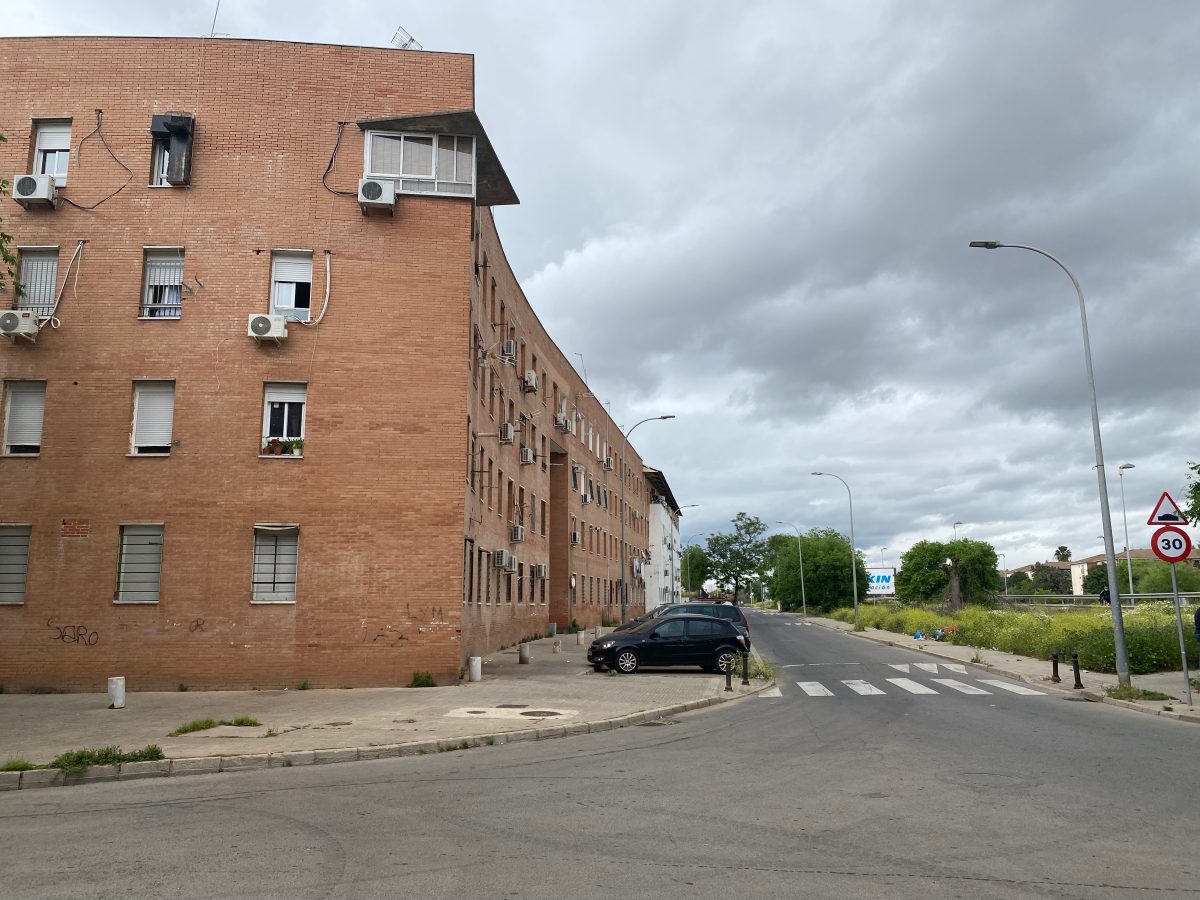
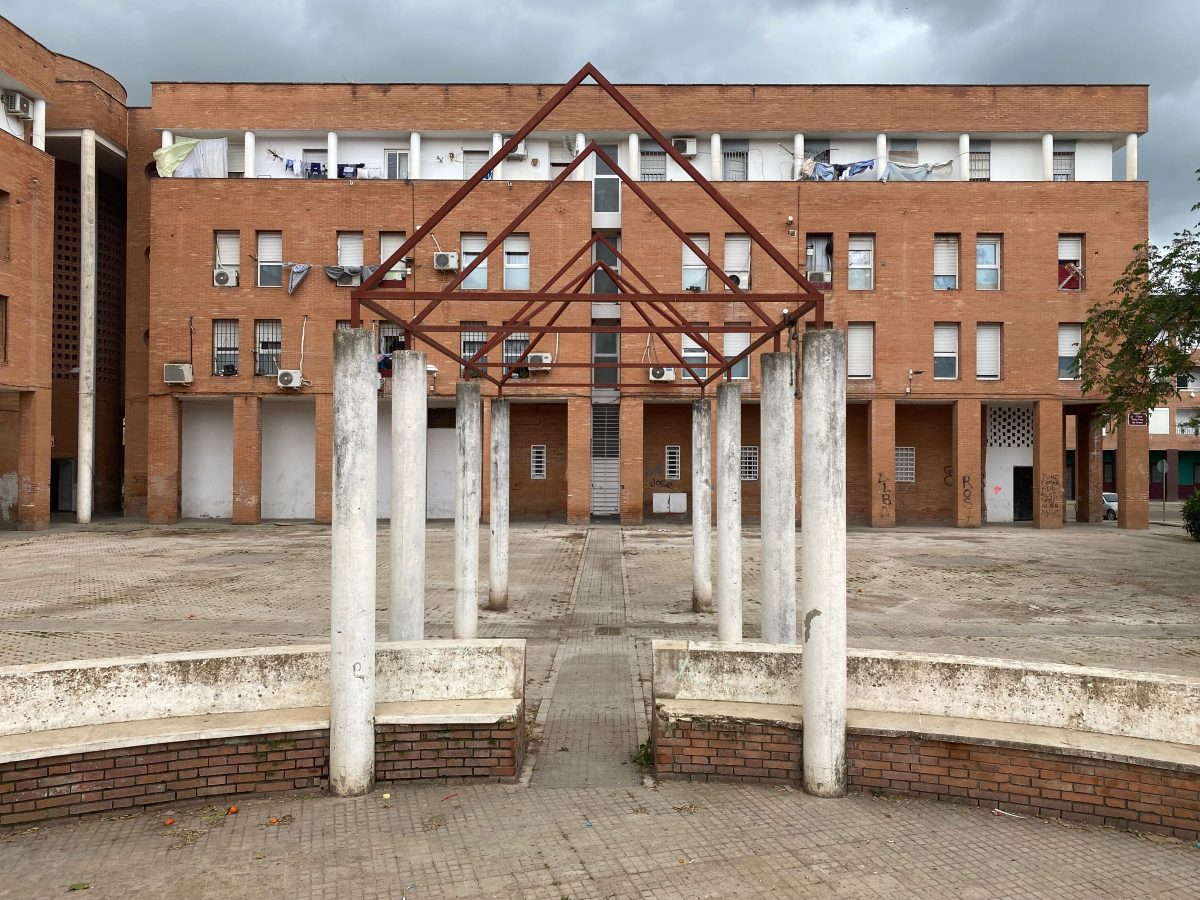
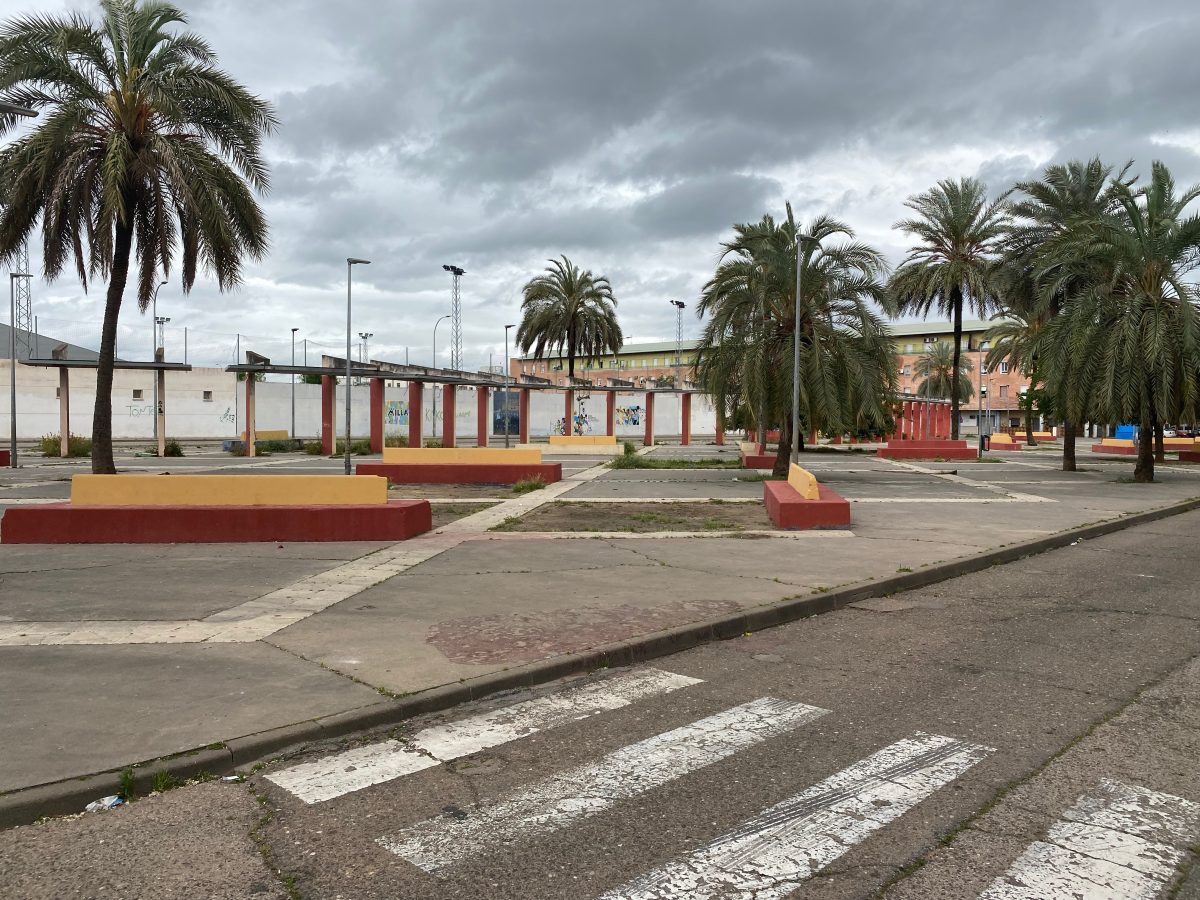
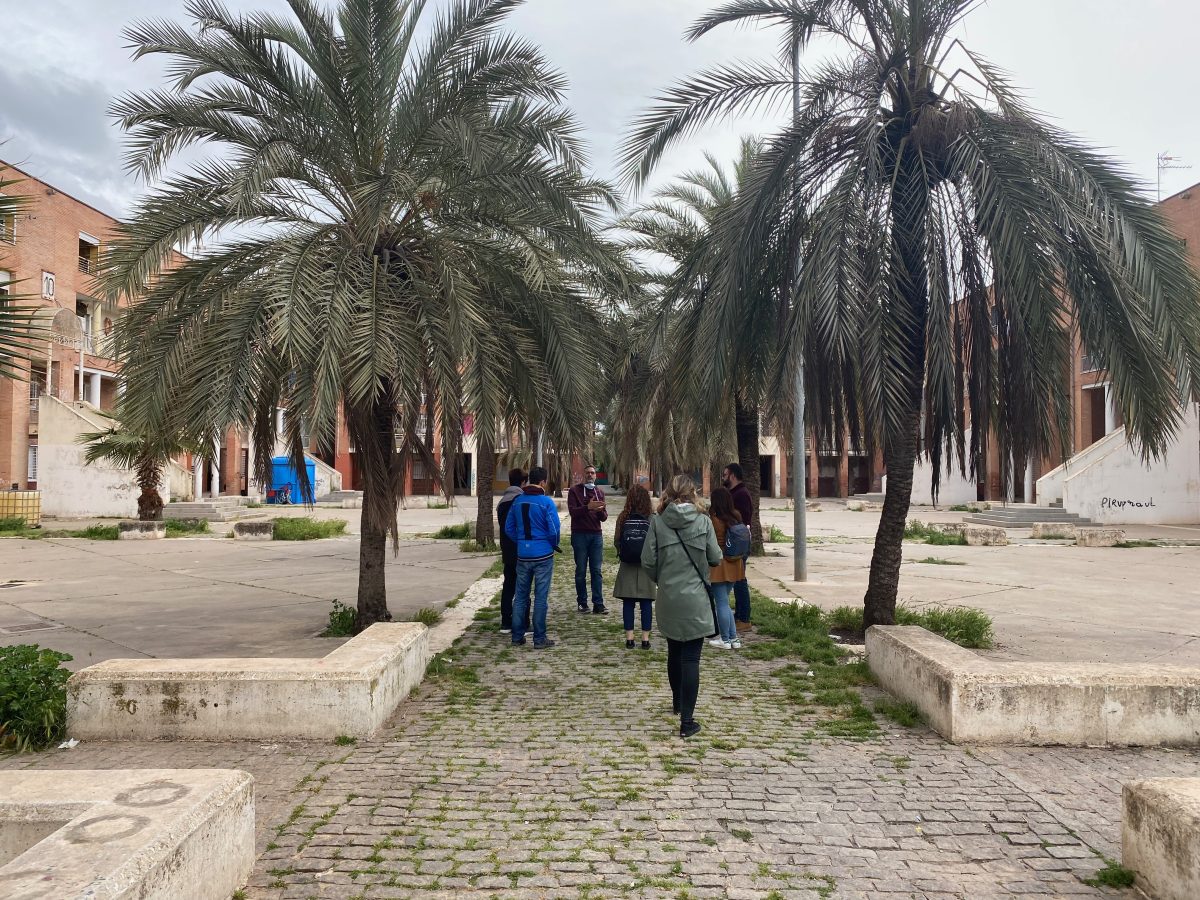
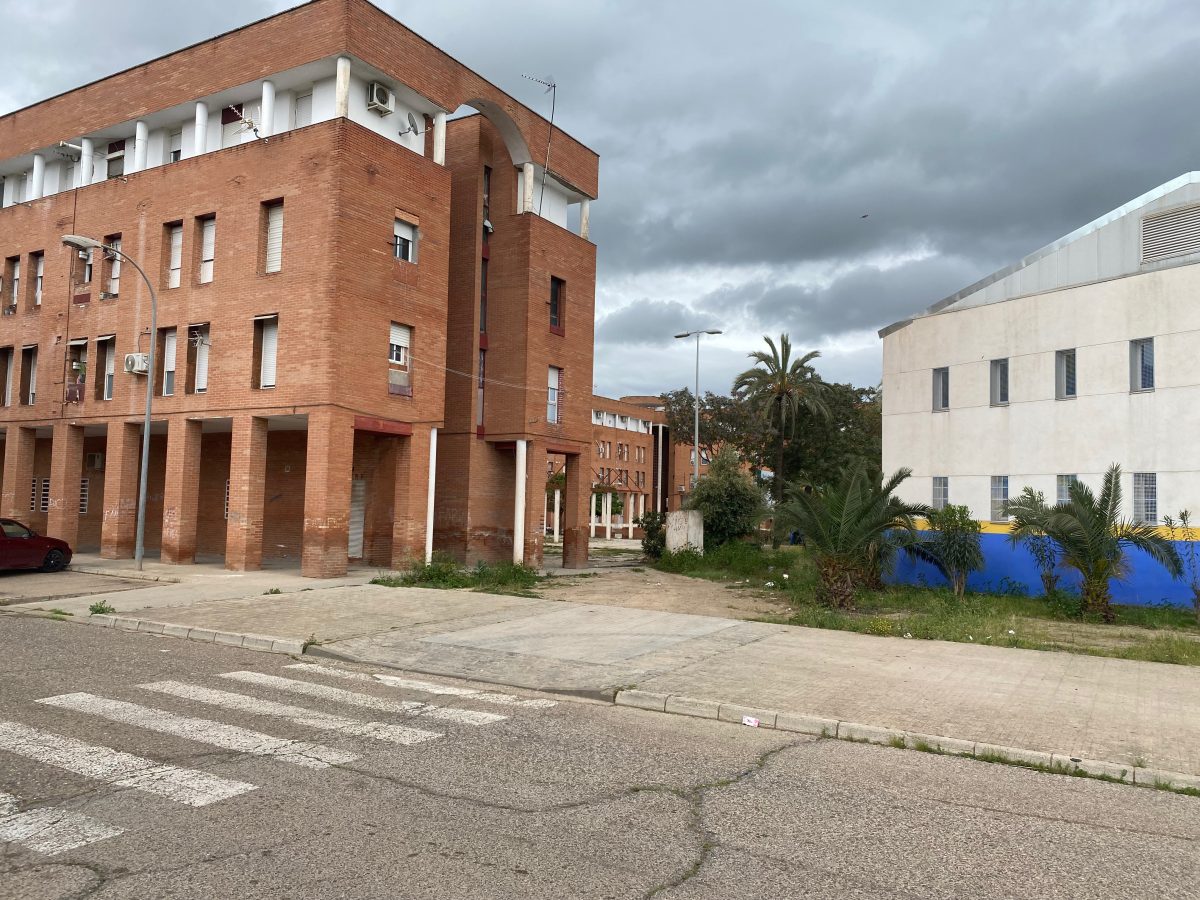
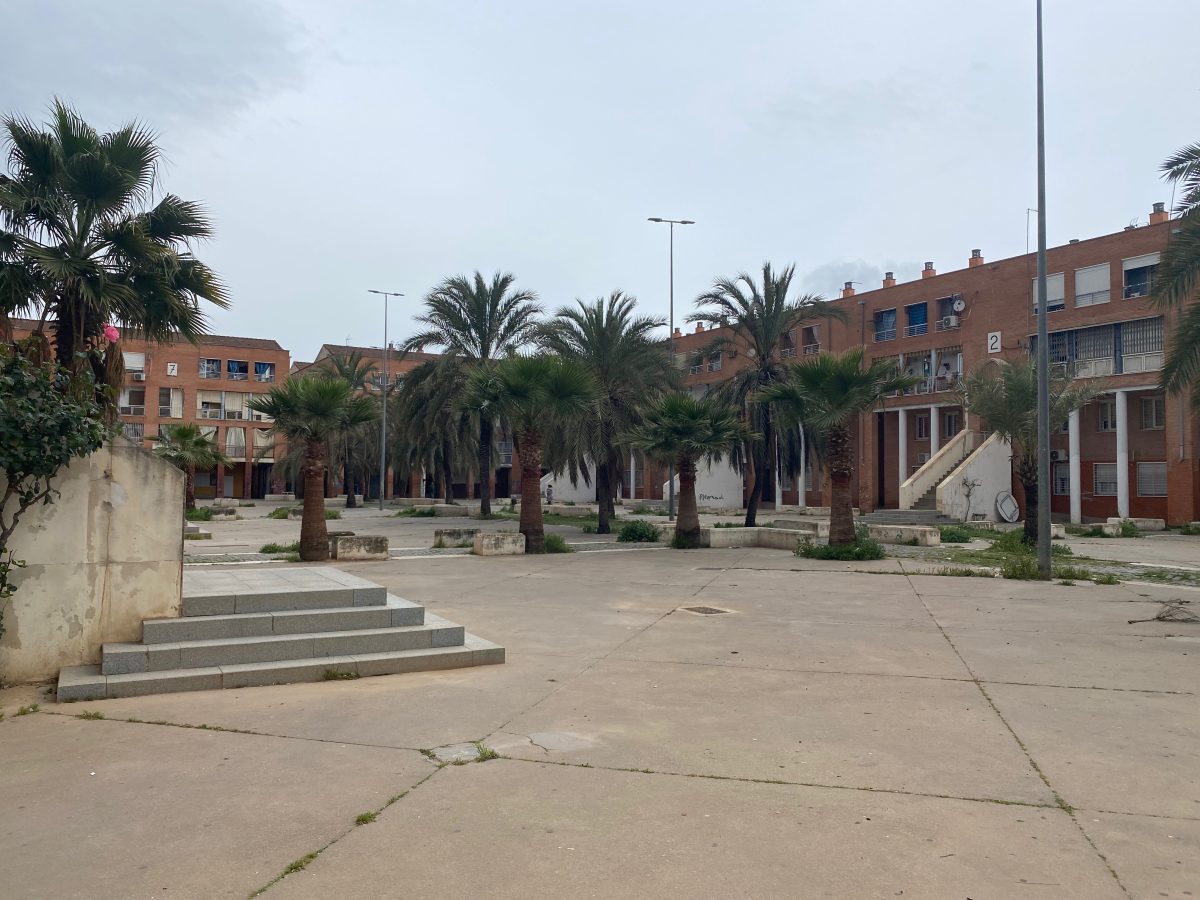
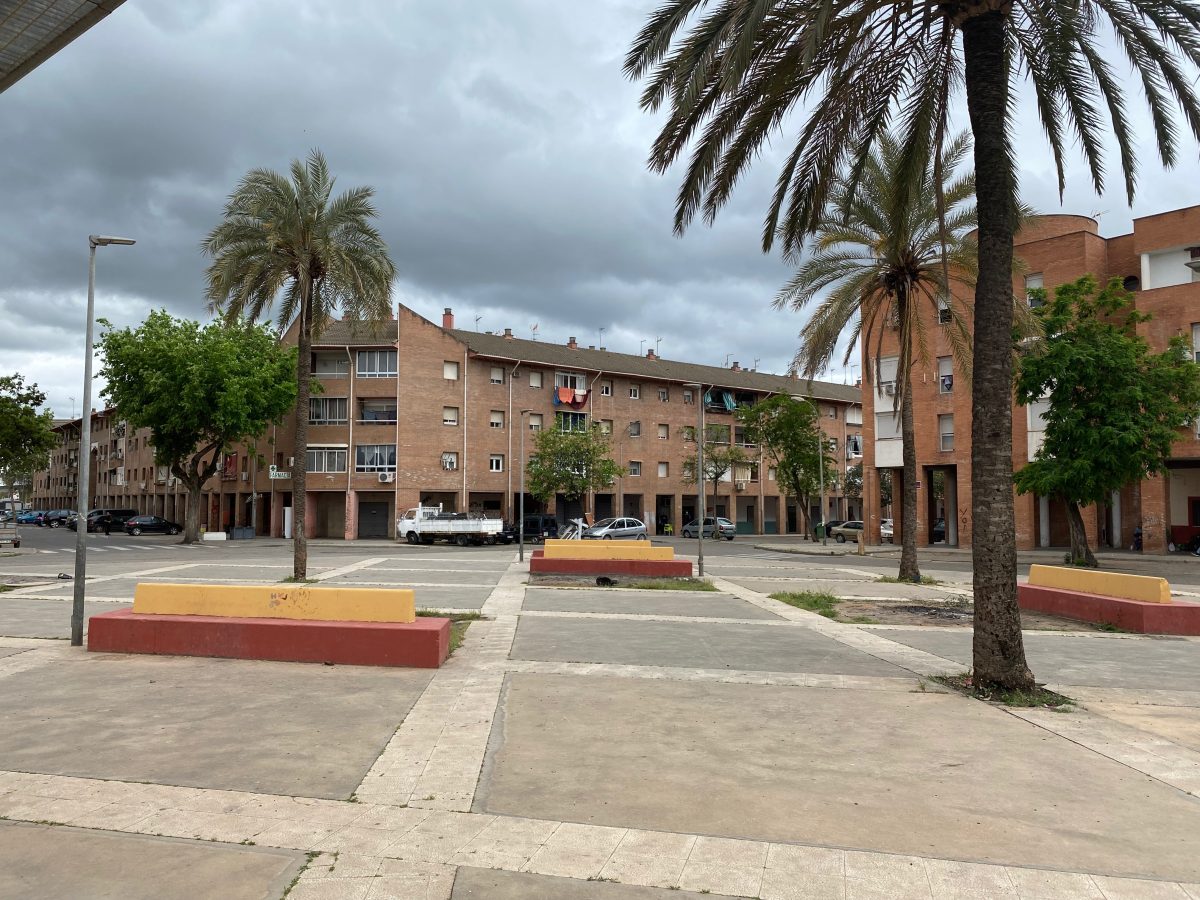
Las Palmeras is a residential neighborhood on the periphery of Córdoba, Andalusia, built in the 1980s and 90s. Recognized as the fourth most deprived neighborhood in Spain, Las Palmeras has struggled over 50 years with high levels of socioeconomic disadvantage.
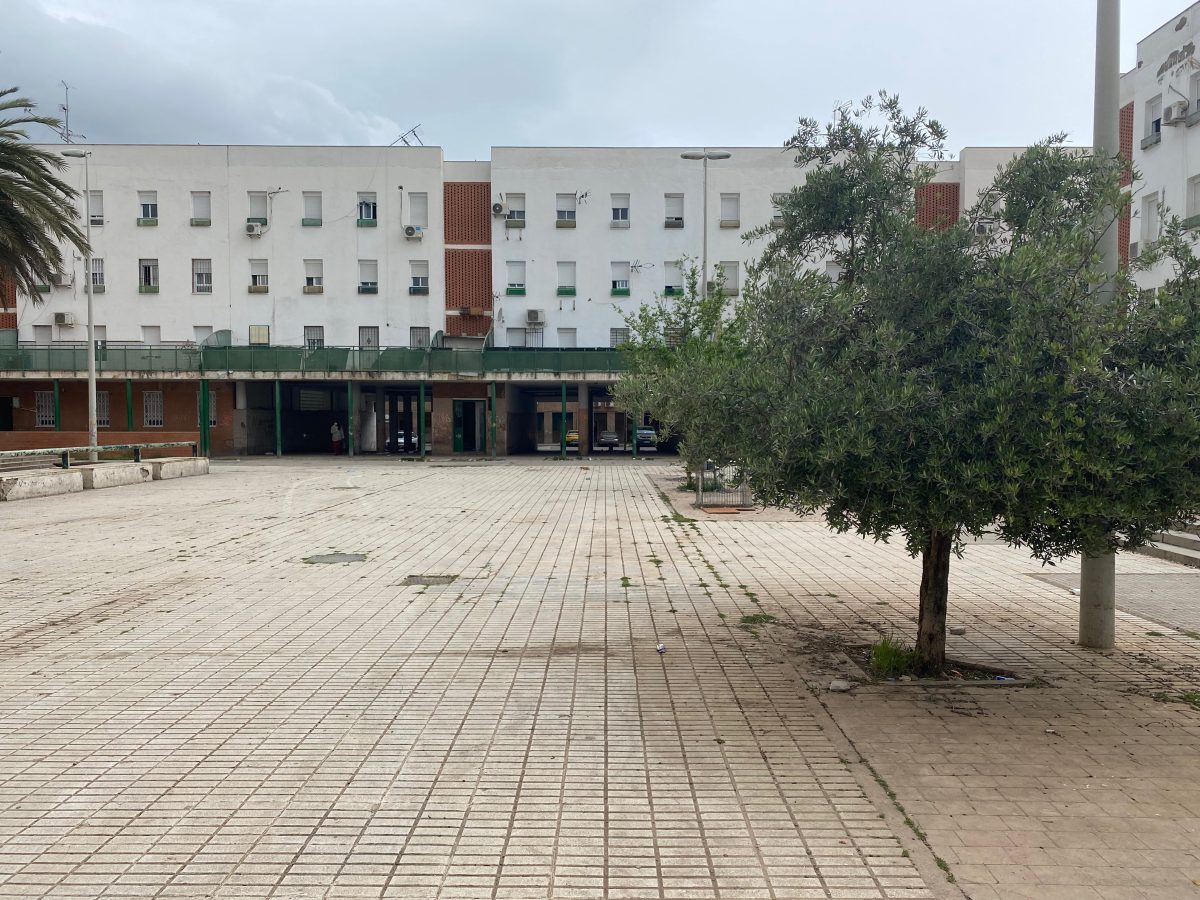
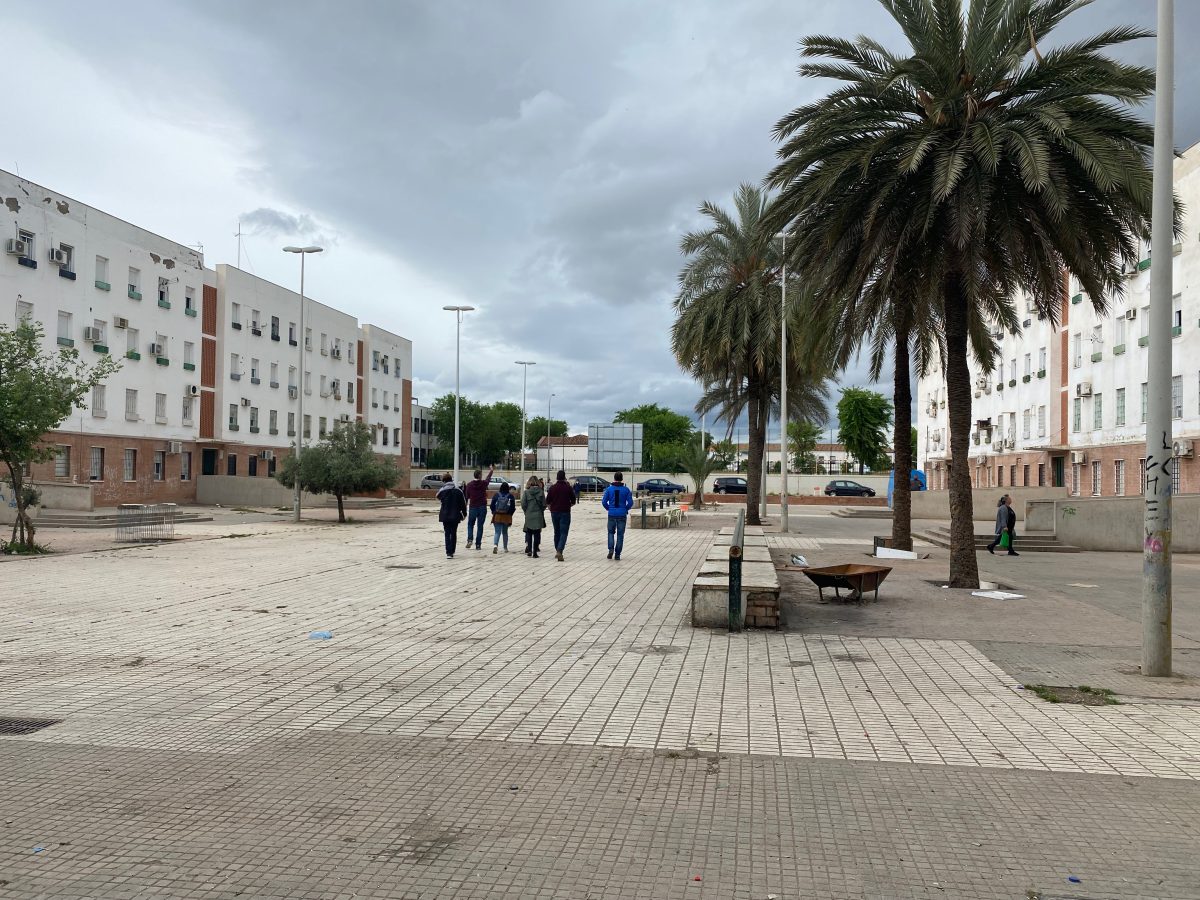
Characterized by multi-story housing blocks built around internal courtyards —patios— Las Palmeras spans roughly 114,000 square meters. As of 2020, it houses 2,212 residents, with a near-equal split of 1,126 men and 1,086 women, representing about 0.6% of Córdoba’s population.
Context
The first settlement in the area dates back to the 1960s when the Municipality built temporary housing for people affected by floods. With Spain’s transition to democracy in the 1970s, the plans for remodeling the neighborhood began in response to demands for decent housing and basic infrastructure, largely championed by neighborhood associations (Asociaciones de Vecinos). It was not until the 1980s—when the housing competencies were assumed by the Junta de Andalucía regional authorities AVRA (Andalucia Housing and Rehabilitation Agency) —that new housing were built in the same area in 5 U-shaped tower blocks around a square called “Patio” reminding of the traditional Córdoba’s architecture. In this initial phase, 104 households were offered housing for rent-to-buy and 615 under the “social rent” system.
From the beginning, Las Palmeras emerged as a neighborhood to place people with low socioeconomic level and facing exclusion problems. During its 50 years of history, the process of structural exclusion has deepened, impacting nearly all residents. The geographical situation, the type of housing and its poor maintenance, the high rates of unemployment and school failure, the social context and the complicated relations between neighbors are structural problems that have led to the neighborhood being stigmatized as an area known for petty criminality and drug abuse.
Project
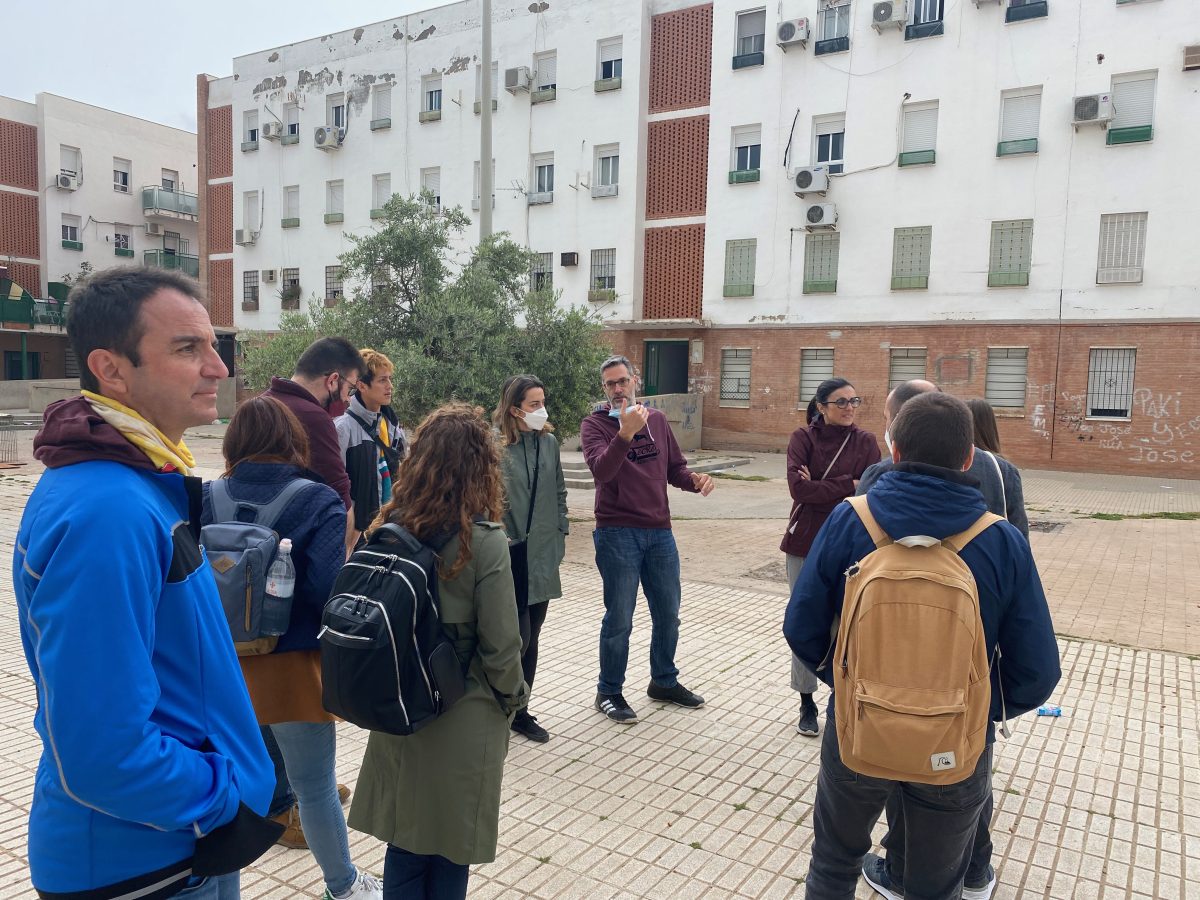
Between 2020 and 2025, Tesserae engaged in Las Palmeras as part of the Horizon 2020 IN-HABIT project. The project aimed to promote inclusive health and wellbeing through context-specific interventions designed and implemented together with residents of Las Palmeras. Although limited in time and scope, the project attempted to unify ongoing efforts in Las Palmeras, promoting cultural and educational activities and improving public space. A notable example is the renaturalization of the Cantarranas stream—once an informal landfill—in which neighbors played a central role in its conception, design, and implementation.
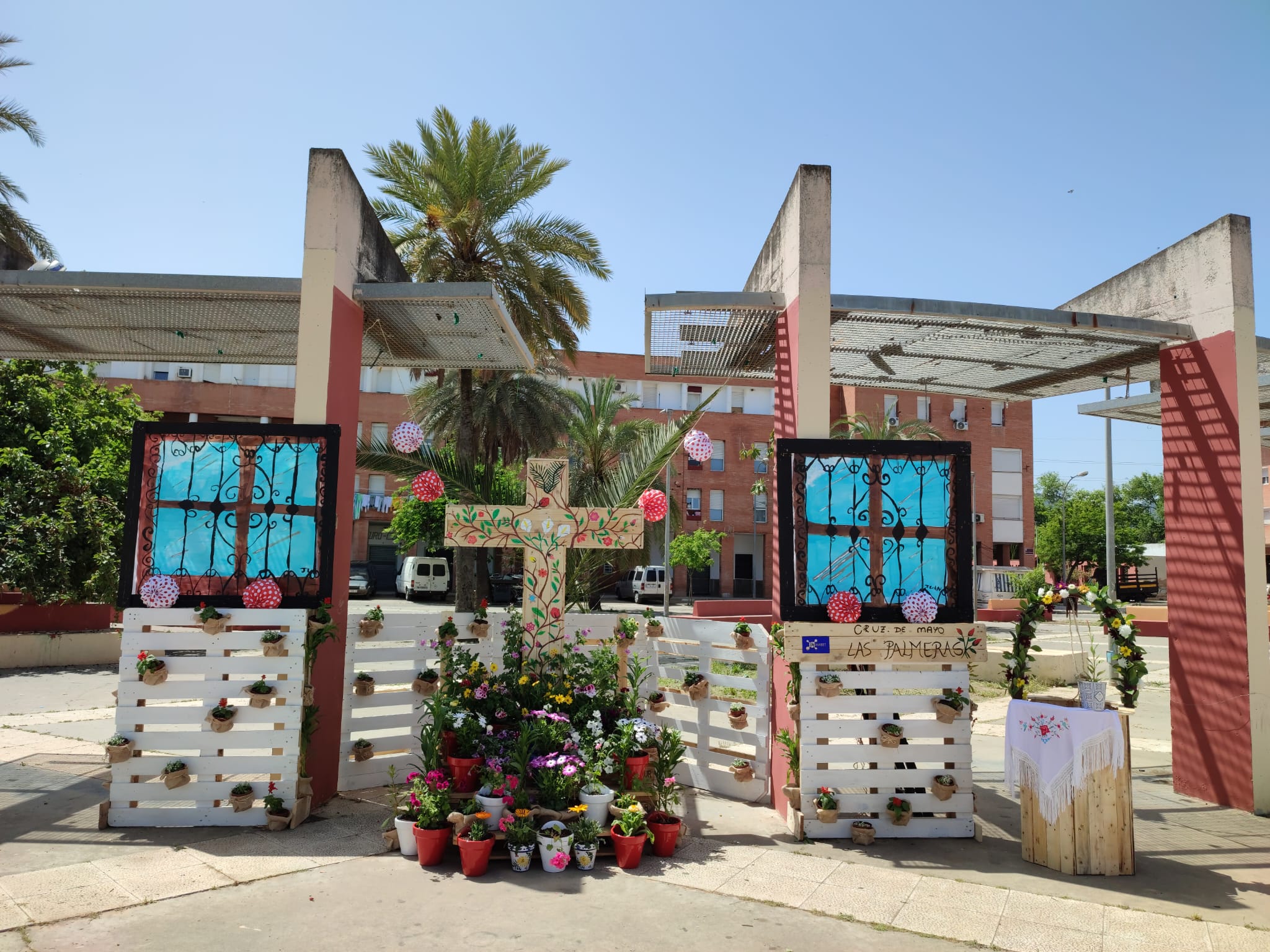
The project also strengthened neighborhood ties by reviving local traditions, such as the Cruz de Mayo, a religious-artistic celebration and La Milla, a running competition. While the engagement of institutional actors with direct responsibility in the public administration was challenging, the collaboration with a wide range of stakeholders, both within and beyond Las Palmeras, succeeded in mobilizing resources and competences towards common goals.
However, deeper structural issues within the neighborhood—such as poor housing quality, unemployment, and lack of basic infrastructure—remain largely unaddressed by the IN-HABIT project although they are fundamental for the genuine goal of achieving inclusive health and well-being.

Read more about Las Palmeras